
(Blog - 5) Job Architecture: The Cornerstone of Digital HR Transformation
Jun 6, 2024
In today's rapidly evolving business environment, organizations face numerous challenges, including technological disruptions and shifting workforce demographics. Amidst these changes, Human Resource (HR) departments play a crucial role in ensuring organizations remain agile, competitive, and capable of attracting and retaining top talent. A key strategy HR leaders are increasingly turning to is the implementation of a well-structured job architecture. This concept, its benefits, and best practices for implementation in Digital HR Transformation are explored in this discussion.
What is Job Architecture?
Job architecture is a strategic framework that systematically classifies jobs within an organization. It serves as a blueprint that defines the roles, responsibilities, and career paths of employees, ensuring consistency, fairness, and transparency across the organization. By establishing clear job definitions, organizations can align employee roles with strategic goals, support career development, and maintain competitive compensation structures.
The Importance of Job Architecture in Modern Organizations
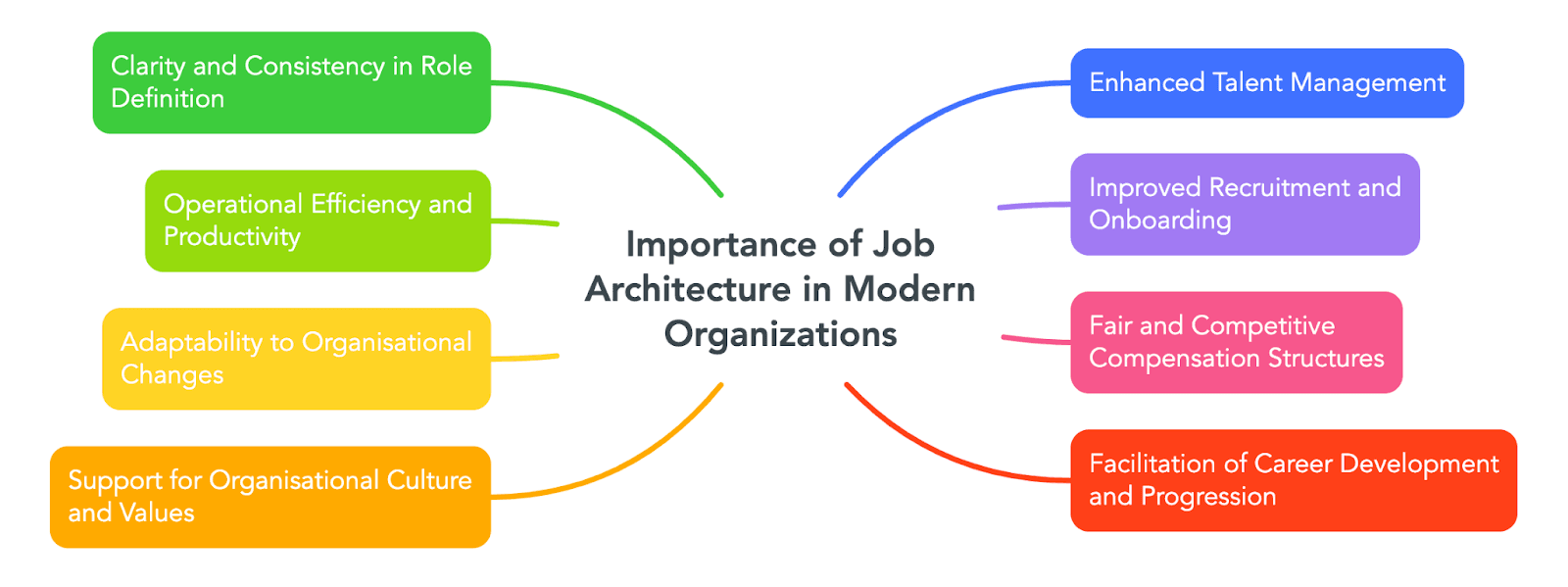
In the dynamic landscape of contemporary business, maintaining a competitive edge requires strategic alignment between an organization’s goals and its workforce capabilities.
Job architecture plays a pivotal role in this alignment for several reasons:
1. Job architecture clarifies roles, fostering transparency and fairness by defining responsibilities, expectations, and qualifications.
2. Enhanced talent management aligns job roles with strategic goals, identifies skill gaps, plans for future needs, and supports targeted skill acquisition through training programs.
3. Improved recruitment and onboarding streamlines processes with clear descriptions, expectations, and responsibilities, reducing time-to-productivity for new hires.
4. Fair compensation structures are developed by defining job levels, aligning pay with market standards, and addressing disparities to foster employee satisfaction and attract top talent.
5. Facilitating career development outlines clear paths, motivating advancement, increasing engagement, and fostering a skilled workforce while reducing turnover.
6. Clear roles enhance operational efficiency by focusing employees, reducing overlap, and improving resource allocation, thereby enhancing productivity and decision-making.
7. Adaptability to organizational changes ensures flexibility, agility, and long-term sustainability through regular updates and responsiveness to new directions and conditions.
8. Support for organizational culture embeds values into job descriptions and criteria, ensuring a positive environment where employees contribute to cohesion and support.
Key Components of Job Architecture
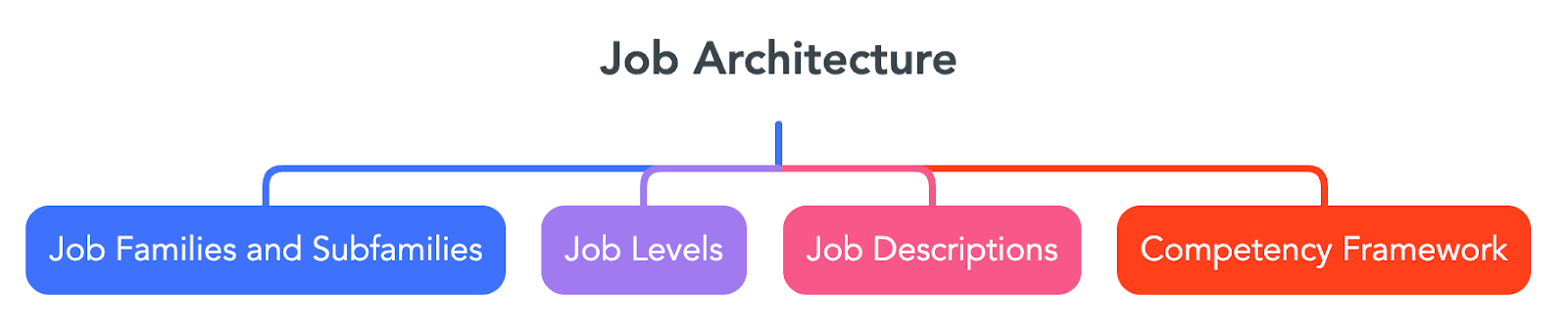
Job Families and Subfamilies:
Job Families: It includes group jobs with similar responsibilities and skills (e.g., Engineering).
Subfamilies: It categorises jobs within families into specific groups (e.g., Software Engineering, Civil Engineering).
Job Levels:
They define hierarchy within job families, indicating progression from entry-level to senior roles. They associate increasing responsibilities, skills, and compensation, aiding career advancement and organizational structure.
Job Descriptions:
They outline primary duties, qualifications, and performance expectations for each role, supporting recruitment, performance management, and career development.
Competency Framework:
It defines necessary skills, behaviours, and attributes for effective job performance, ensuring alignment with organizational goals and facilitating employee growth.
Best Practices for Implementing Job Architecture in Digital HR Transformation:

Develop a Comprehensive Plan:
Outline a structured approach with goals, timelines, and KPIs for integrating job architecture with digital HR tools.
Engage Stakeholders Early:
Involve HR, IT, and other key stakeholders early for alignment and collaboration.
Leverage Technology:
Leverage AI, machine learning, and big data analytics to enhance job architecture capabilities and predict workforce needs.
Focus on User Experience:
Prioritise intuitive digital tools and provide training for smoother adoption by employees and HR staff.
Monitor and Refine:
Continuously monitor effectiveness, gather user feedback, and refine the system for ongoing relevance and satisfaction.
Conclusion
Integrating robust job architecture with digital HR tools facilitates adaptability, clarity, and alignment in HR processes, supporting long-term organizational success. Despite challenges, prioritising user experience and following best practices ensures a smooth transition and optimises HR functions for sustained growth and competitive advantage in the digital era.
About the authors:
Monalika Sahoo is the HR Manager at Future of HR, Inc. She is also pursuing a postgraduate degree in Anthropology from IGNOU, New Delhi, showcasing her dedication to understanding human cultures and enhancing organizational dynamics.
Muthu Kumar Hanu, aka MK, is a Global HR Technology Executive and co-founder of Future of HR, Inc. Certified in multiple HR and technology domains, MK specializes in mentoring startups and driving organizational change through strategic HR interventions.
Navtesh Dhir is a Product and UX Designer based in Ontario, Canada. He is dedicated to creating user-centric solutions that drive societal impact and foster innovation in public service.
For more information, please reach out to us at hey@futureofhrinc.com.
